Definition: An odontogenic epithelium neoplasm with a thin keratinized lining.
Radiographic Features:
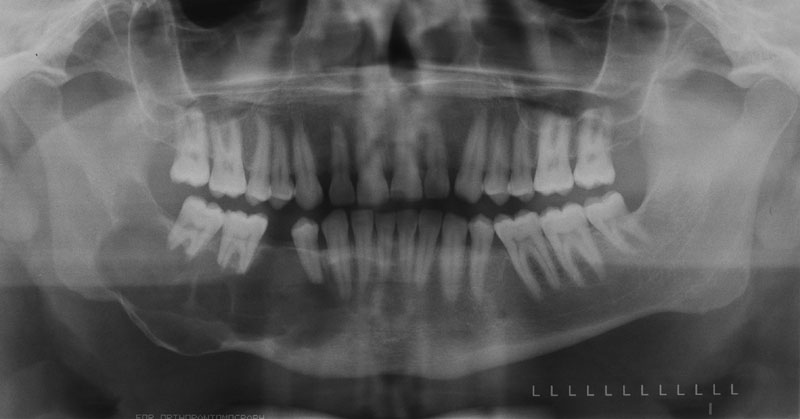
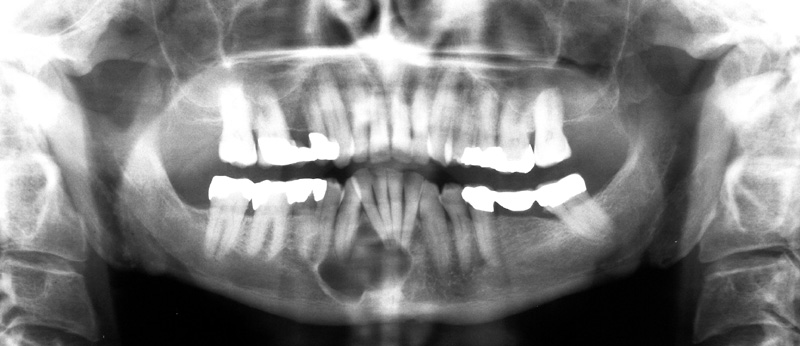
Location: Posterior mandible and ramus (most common) but can occur anywhere in the maxilla or mandible.
Edge: Well-defined to well-localized.
Shape: Round to no identifiable shape.
Internal: Radiolucent (unilocular or multilocular).
Other: Tendency to grow along the jaw with minimal expansion.
Number: Single. If multiple, an underlying syndrome should be considered (basal cell nevus syndrome/Gorlin-Goltz syndrome).
(Click image to enlarge)
Odontogenic keratocyst – right posterior mandible
Odontogenic keratocyst – anterior mandible
How to distinguish between ameloblastoma and keratocystic odontogenic tumor on radiology,as they are both cause expansion and root resorption of adjacent teeth?
Thanks
Ameloblastoma – tends to cause more resorption of teeth and expansion of bone first.
Keratocystic odontogenic tumor – grows along jaws first.
But since both have very similar radiographic appearances and locations that they occur you should always have both of them in a differential list if you are considering one of them.
how to get rid off of this. is it complicated (keratocystic odontogenic tumor )
It depends on location, size and other surrounding anatomical structures. Typically enucleation is done but each case is slightly different.