This week is all about the basics of horizontal bone loss and vertical bone defects on radiographs.
Horizontal Bone Loss
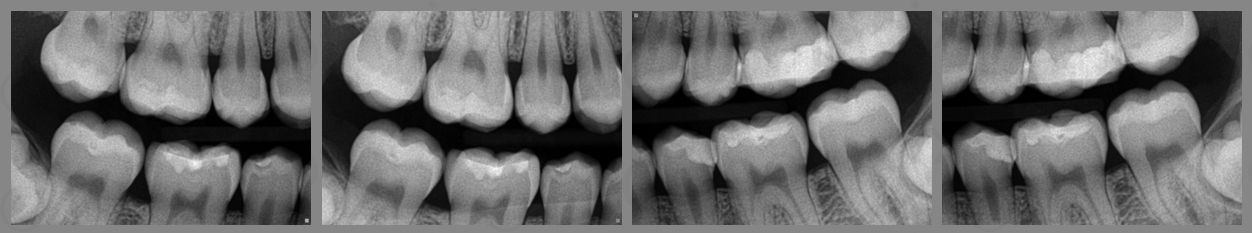
When identifying horizontal bone loss you must first go through the same steps of evaluating normal bone appearances (last weeks post). The two lines (adjacent cemento-enamel junctions and crest of the alveolar ridge) will still be parallel.
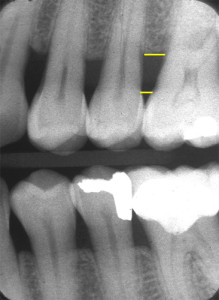 The only difference for horizontal bone loss is that the crest of the alveolar ridge is more than 2 mm apical from the cemento-enamel junction.
The only difference for horizontal bone loss is that the crest of the alveolar ridge is more than 2 mm apical from the cemento-enamel junction.
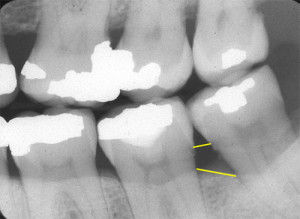
Vertical bone defects present when the line from the adjacent cemento-enamel junctions and the line of the crest of the alveolar ridge are NOT PARALLEL. The vertical bone defect is typically described by the tooth and surface where more bone loss is evident.
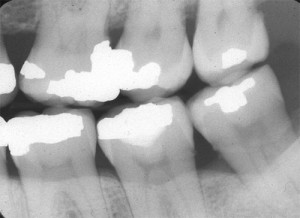 If you note the bone between the mandibular second and third molar appears to have two different crests seen. This is an example of cortical plate loss which will be covered next week. 😀
If you note the bone between the mandibular second and third molar appears to have two different crests seen. This is an example of cortical plate loss which will be covered next week. 😀
Next week: Cortical plate loss and furcation involvement
If you have any questions or comments, please leave them below. Thanks and enjoy!
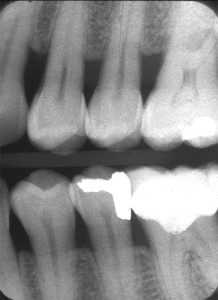

very helpful …thanks a lot for the post
Thanks. I’m glad to hear you are finding this helpful. 🙂
sir give a radiological interpretation for freshly extracted tooth socket
I’ll try to find one and post it so all can see what it appears like. Thanks. 🙂