Definition: Resorption of the outer surface of a tooth.
Radiographic Features:
Location: Most commonly seen at the apices of teeth, but can affect any portion of a tooth that is within bone.
Edge: Well-defined, smooth outline with altered shape of the tooth.
Shape: Blunted, linear apex instead of tapered.
Internal: Radiolucent when appears over the root.
Other: When positioned over the pulp chamber and/or root canal, the outline of the chamber/canal will still be evident.
Number: May be single or multiple.
TIP: External resorption over the facial or lingual surface of a root can be difficult to determine from internal resorption. Re-examine the radiograph to determine if the outline of the pulp chamber and/or root canal is visible. A shift shot can help determine if the chamber/canal outline is evident and not continuous with the radiolucent area. If the radiolucent area is continuous with the chamber/canal outline, it indicates internal resorption is more likely.
(click image to enlarge)
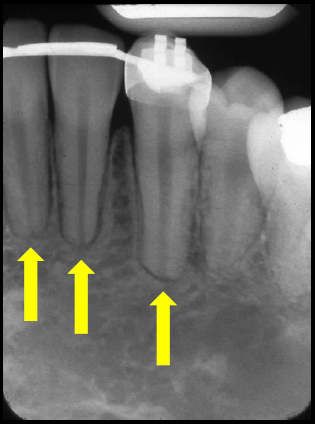
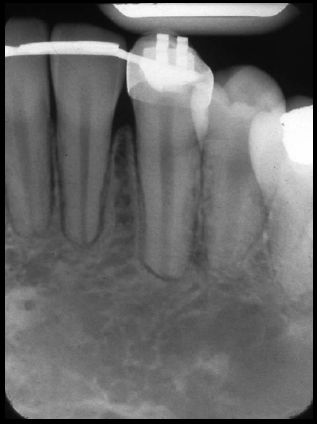
External resorption at apices of mandible anterior teeth
(left – with arrows) (right – without arrows)
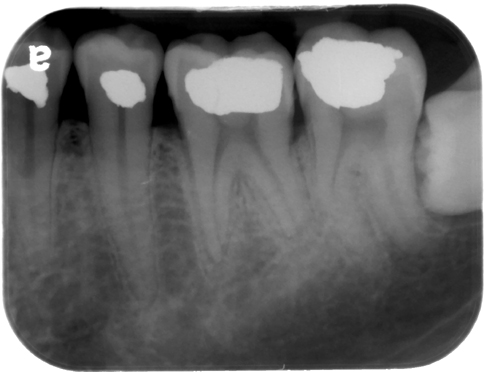
External resorption
(blunted apices of mandibular left first molar – #19)
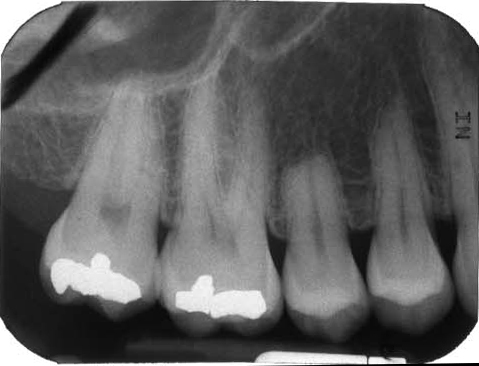
External resorption
(apex and over root – note root canal outline evident)
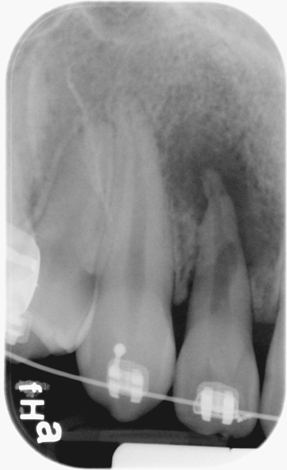
External resorption
(blunted apex of maxillary right second premolar -#4)
External resorption
(impacted maxillary right third molar – #1)
Thank you for sharing!
You’re welcome. 🙂