Definition: The non-physiologic wearing of the teeth. This can be caused by toothbrushes, hairpins, toothpicks and many more.
Radiographic Features:
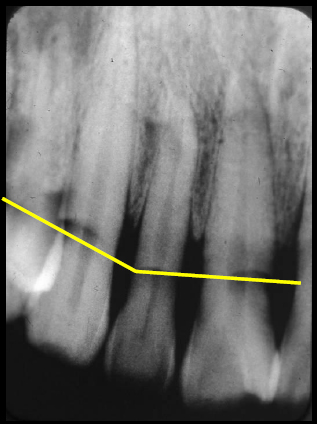
Location: Seen in the cervical region on the facial surfaces when caused by a toothbrush. Toothpick abrasion tends to be interproximal. Hairpin abrasion is seen on the incisal edges.
Edge: Well-defined with a portion of tooth missing where the object is frequently placed.
Shape: Toothbrush abrasion – linear. Other abrasion will have the same shape as the object that is wearing away the tooth structure.
Internal: Radiolucent area where tooth structure is missing.
Other: None.
Number: May be single or multiple.
(click image to enlarge)
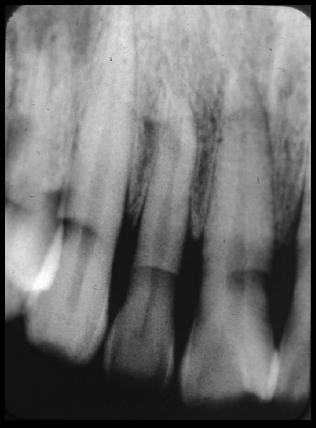
Toothbrush abrasion
(left – yellow line showing radiolucent area in cervical region of tooth) (right – without yellow line)
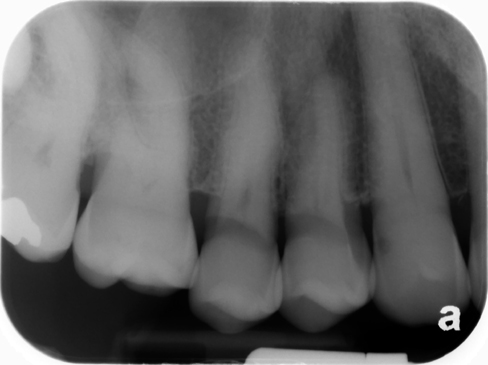
Toothbrush abrasion
(note the linear radiolucent area on the premolars)
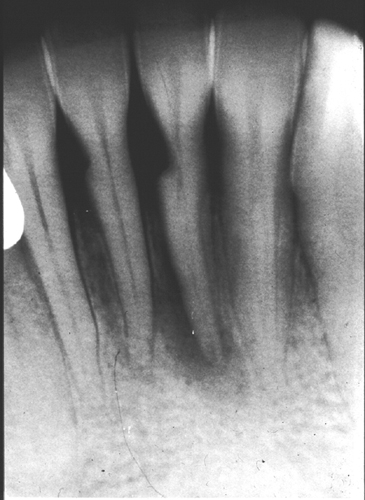
Toothpick abrasion
(note the notch between the central incisors due to frequent placement of a toothpick)
very impressive
Thanks. 🙂
How can you tell between abrasion and root caries?
Abrasion will follow the cemento-enamel junction giving it a curved radiolucent band appearance. It will also typically involve the adjacent teeth. There are still times if only one tooth is involved that it is difficult to determine the difference between root caries and abrasion.