Definition: A buccal bifurcation cyst is an uncommon inflammatory cyst of the mandibular molars.
Clinical Features: It is most commonly found in individuals under the age of 20. Clinically the lingual cusps may project higher than the buccal cusps of the associated tooth. Other names it is referred to as include a paradental cyst and mandibular infected buccal cyst.
Radiographic Features:
| 2D | CBCT | |
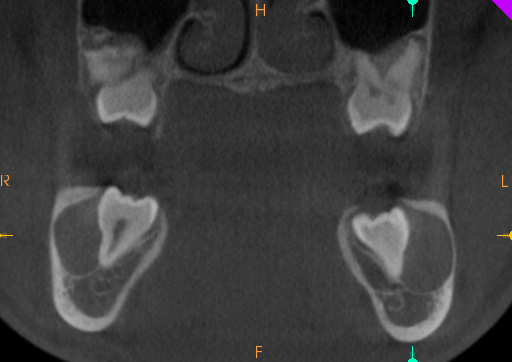
| Location: | Furcation region. Most common – permanent first mandibular molar. Less common – second and third molars. | Furcation region. Most common – permanent first mandibular molar. Less common – second and third molars. |
| Edge: | Well-defined. +/- corticated | Well-defined. +/- corticated |
| Shape: | Round to ovoid. | Round to ovoid. |
| Internal: | Radiolucent, unilocular. | Radiolucent, unilocular. |
| Other: | The adjacent teeth are vital and tipped with the roots towards the lingual. This will be evident in the mouth as the lingual cusps will appear higher than the buccal cusps. It may displace or resorb adjacent teeth as it enlarges. | The adjacent teeth are vital and tipped with the roots towards the lingual. This is best seen on coronal and cross-sectional views. It may displace or resorb adjacent teeth as it enlarges. |
| Number: | Single or multiple. | Single or multiple. |
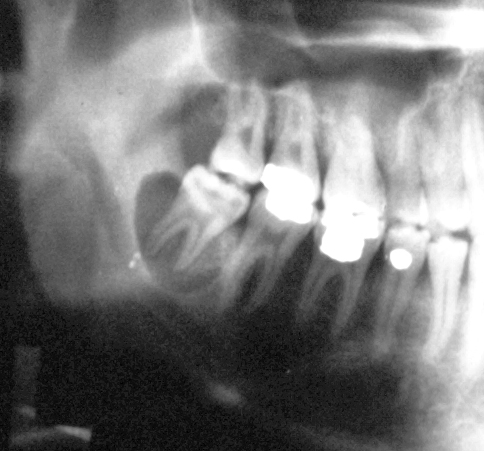
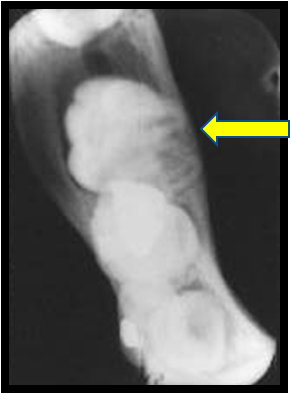
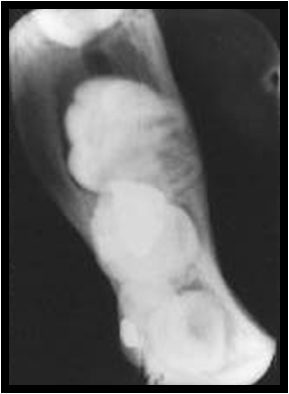
Buccal Bifurcation Cyst – 2D
Buccal Bifurcation Cyst on occlusal radiographs with arrow showing tipping of roots.
Buccal Bifurcation Cyst – CBCT
One thought on “Buccal Bifurcation Cyst”