Definition: Excessive deposition of cementum on tooth roots.
Radiographic Features:
Location: At the apex of a tooth.
Edge: Well-defined.
Shape: Root will have a bulbous shape at apex instead of tapering to a point as it typically does. The outline may be smooth or irregular.
Internal: Radiopaque. Radiopacity is less than dentin.
Other: The periodontal ligament space will be continuous around the bulbous root indicating the radiopaque area is attached to the root.
Number: May be single or multiple. When multiple teeth are effected with an irregular outline, Paget’s disease of bone may be an underlying cause.
(click image to enlarge)
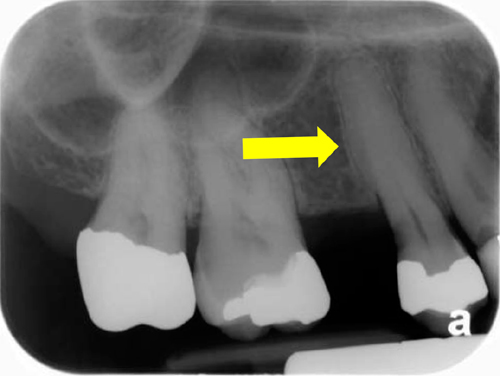
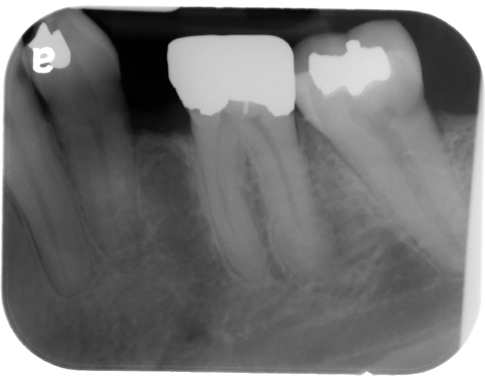
hypercementosis
(note the bulbous, irregular shape of the maxillary premolar)
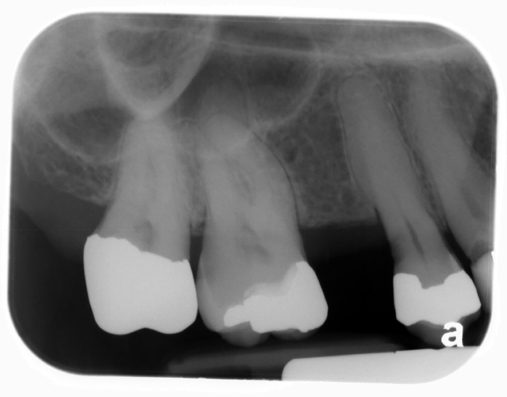
hypercementosis
(note the bulbous root of the maxillary left second premolar – #13)
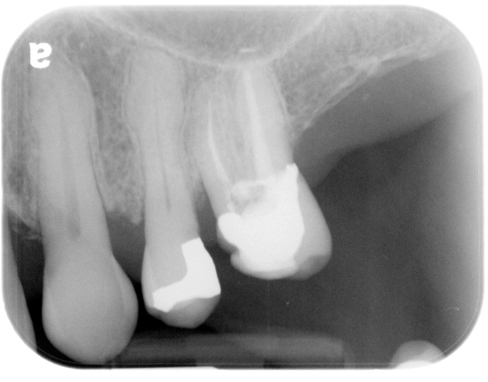
hypercementosis
(maxillary right canine – #6)
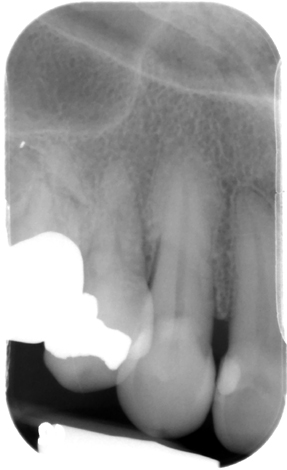
hypercementosis
(distal root of the mandibular left first molar – #19)
thank you 🙂 concise and full of usefull information
hi Dr G.
x ray belong to maxillary right canine, does not it look like enostosis? or focal osteosclerosis? I can not differentiate it.
it is a bit different from other examples to me.
thanks a tone.
If you look closely at maxillary right canine you will see a thin radiolucent line around the radiopaque area that is continuous with the periodontal ligament space of the canine indicating it is attached to the tooth root and not a hyperplasia of bone (enostosis or focal idiopathic osteosclerosis).
Hi Doc G!
The radiographs are great for understanding! Thank you so very much Doc!