Increased density
- E (increased exposure to x rays)
E =↑ Exposure (x rays)
This occurs when the phosphor plate is overexposed (i.e. using a molar setting for an anterior radiograph).
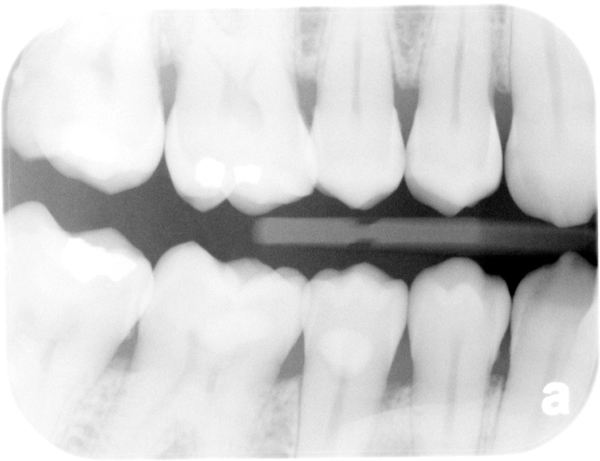
Increased density due to incorrect time setting.
Decreased density
- E (decreased exposure to x rays)
- E (increased exposure to visible light)
- B (bending)
E = ↓Exposure (x rays)
This occurs when the phosphor plate is underexposed or not exposed at all. There are two ways this can occur. The first is decreased time of radiographic exposure (i.e. using a anterior time setting for a molar radiograph) creating an overall whiter image.
Overall decreased density due to incorrect time setting.
The second is by incorrect alignment with the PID/cone such that the entire phosphor plate is not exposed to x rays. This will result in a white area of the final image where no x rays exposed the phosphor plate. This white area may have a straight edge (rectangular PID) or a curved edge (round PID).
Rectangular cone cut on left.
E =↑ Exposure (visible light)
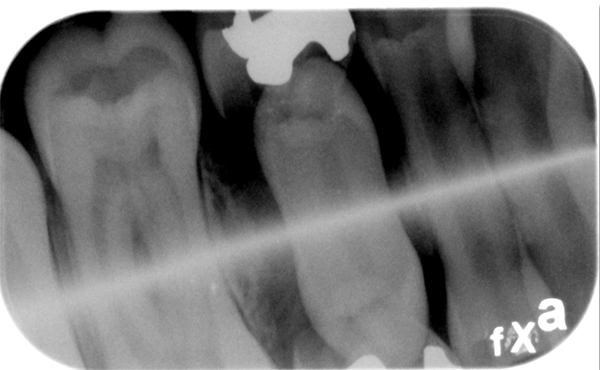
This occurs when the phosphor plate is exposed to visible light for prolonged periods of time. This will result in a white area where the visible light exposed the plate.
Decreased density due to visible light exposure.
B = Bending
This is pretty straight forward and it means that there is a bend of the phosphor plate. This results in a white line or area of the image.
White line due to bending.
If you have any questions, please let me know.
Thanks and enjoy!